GCP setup guide
The following is a set of instructions to quickstart DataHub on GCP Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Note, the guide assumes that you do not have a kubernetes cluster set up. If you are deploying DataHub to an existing cluster, please skip the corresponding sections.
Prerequisites
This guide requires the following tools:
- kubectl to manage kubernetes resources
- helm to deploy the resources based on helm charts. Note, we only support Helm 3.
- gcloud to manage GCP resources
Follow the following guide to correctly set up Google Cloud SDK.
After setting up, run gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com to make sure GKE service is enabled.
Start up a kubernetes cluster on GKE
Let’s follow this guide to create a new cluster using gcloud. Run the following command with cluster-name set to the cluster name of choice, and zone set to the GCP zone you are operating on.
gcloud container clusters create <<cluster-name>> \
--zone <<zone>> \
-m e2-standard-2
The command will provision a GKE cluster powered by 3 e2-standard-2 (2 CPU, 8GB RAM) nodes.
If you are planning to run the storage layer (MySQL, Elasticsearch, Kafka) as pods in the cluster, you need at least 3 nodes with the above specs. If you decide to use managed storage services, you can reduce the number of nodes or use m3.medium nodes to save cost. Refer to this guide for creating a regional cluster for better robustness.
Run kubectl get nodes to confirm that the cluster has been setup correctly. You should get results like below
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
gke-datahub-default-pool-e5be7c4f-8s97 Ready <none> 34h v1.19.10-gke.1600
gke-datahub-default-pool-e5be7c4f-d68l Ready <none> 34h v1.19.10-gke.1600
gke-datahub-default-pool-e5be7c4f-rksj Ready <none> 34h v1.19.10-gke.1600
Setup DataHub using Helm
Once the kubernetes cluster has been set up, you can deploy DataHub and it’s prerequisites using helm. Please follow the steps in this guide
Expose endpoints using GKE ingress controller
Now that all the pods are up and running, you need to expose the datahub-frontend end point by setting up ingress. Easiest way to set up ingress is to use the GKE page on GCP website.
Once all deploy is successful, you should see a page like below in the "Services & Ingress" tab on the left.
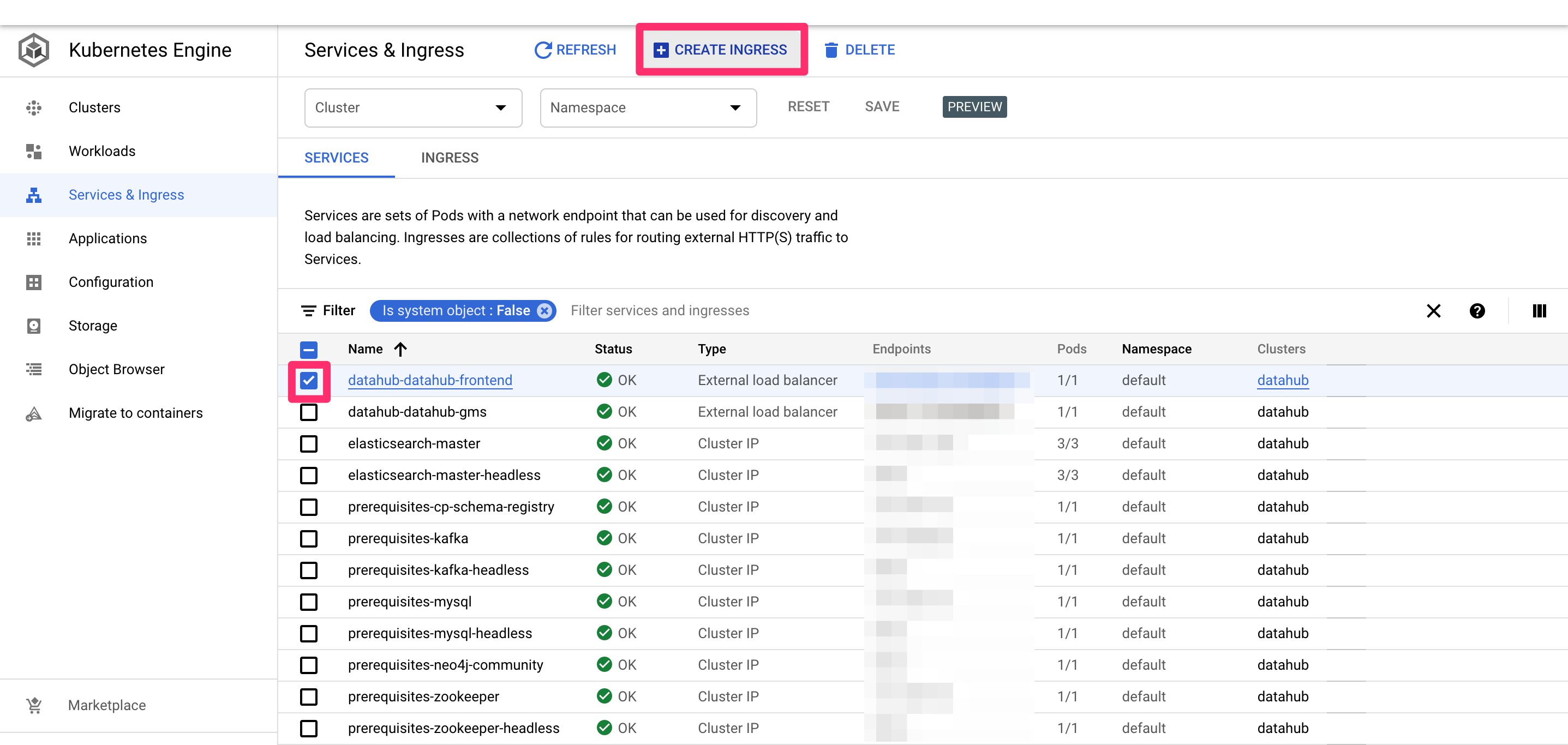
Tick the checkbox for datahub-datahub-frontend and click "CREATE INGRESS" button. You should land on the following page.
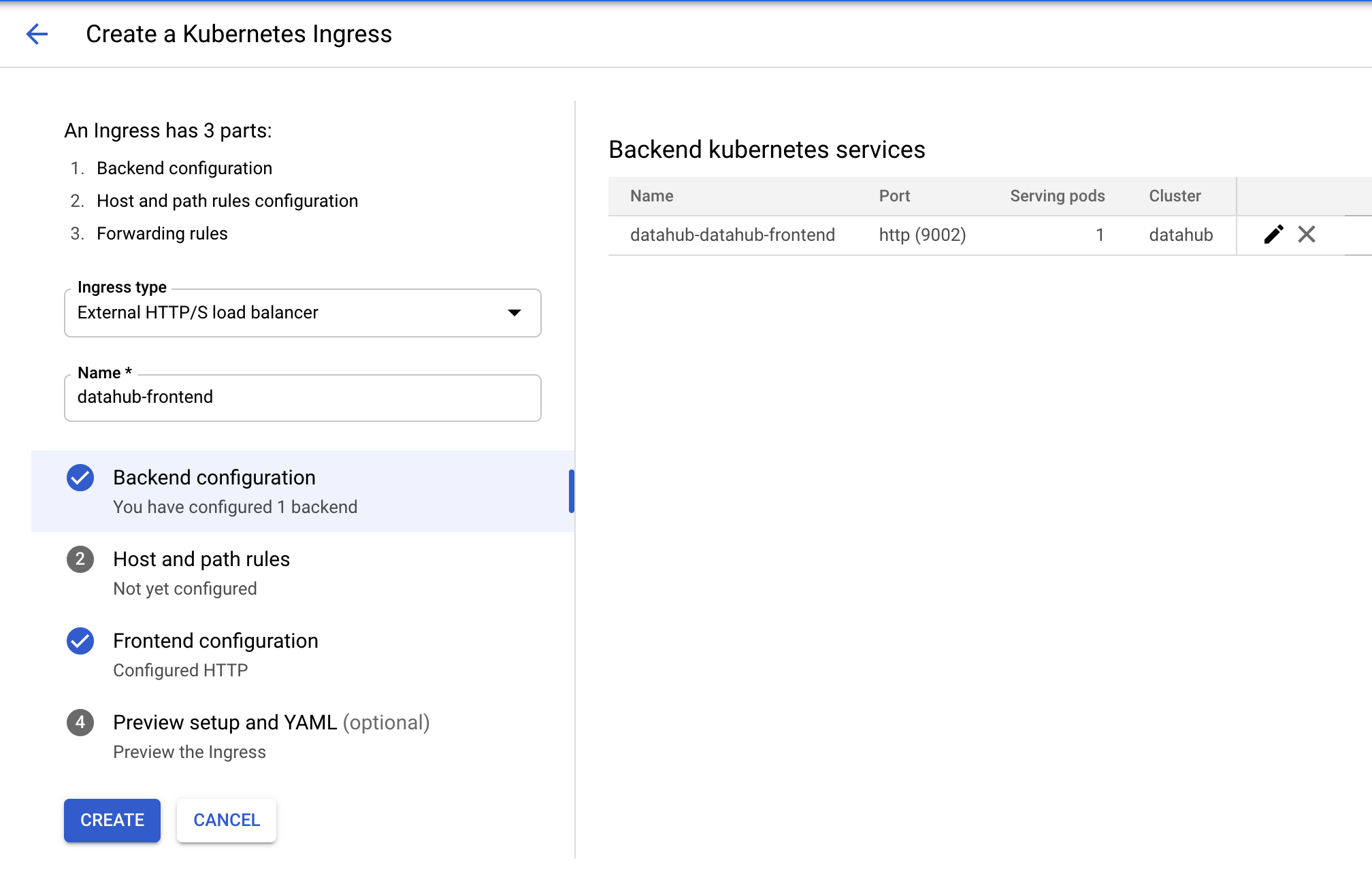
Type in an arbitrary name for the ingress and click on the second step "Host and path rules". You should land on the following page.
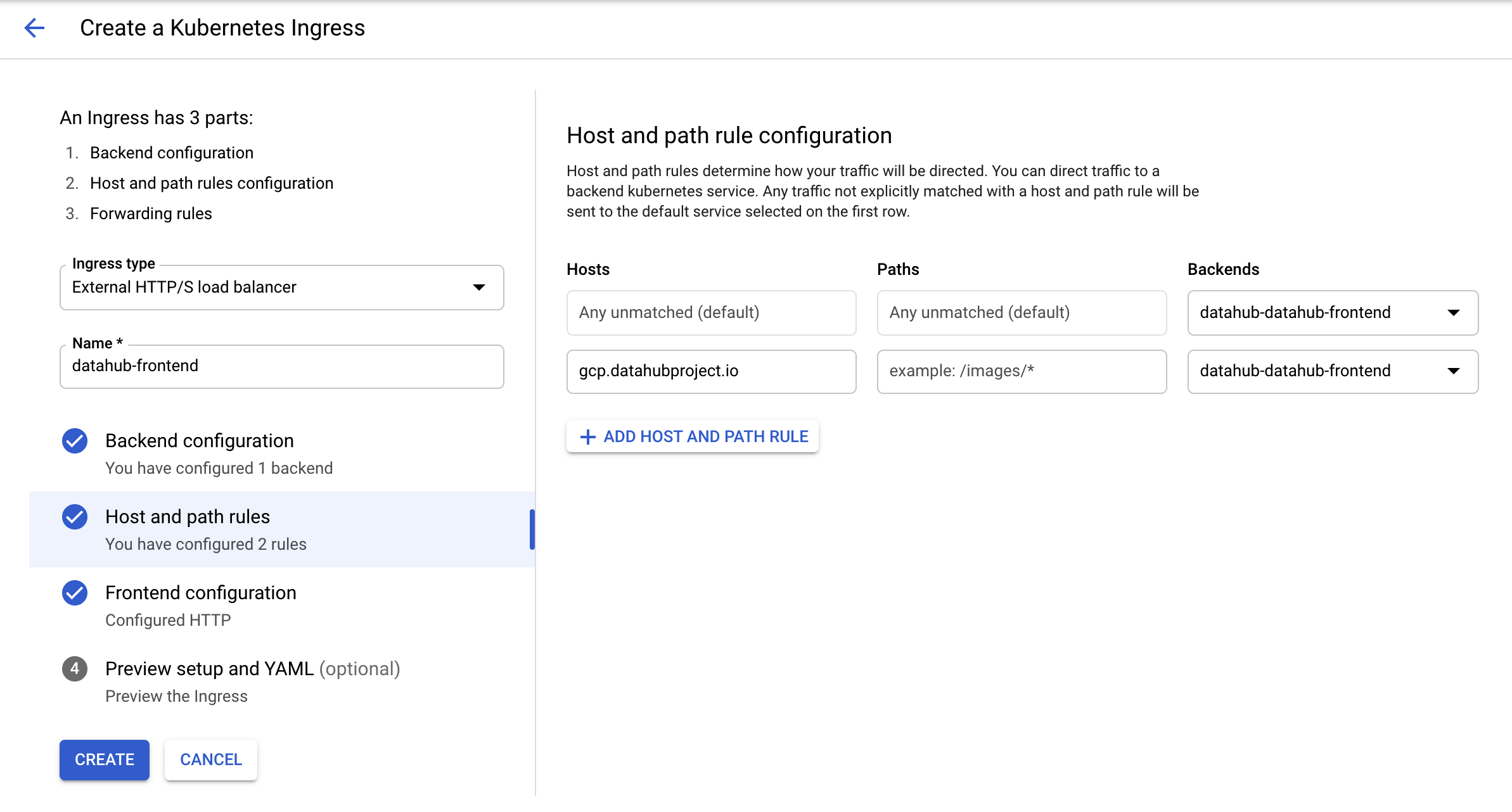
Select "datahub-datahub-frontend" in the dropdown menu for backends, and then click on "ADD HOST AND PATH RULE" button. In the second row that got created, add in the host name of choice (here gcp.datahubproject.io) and select "datahub-datahub-frontend" in the backends dropdown.
This step adds the rule allowing requests from the host name of choice to get routed to datahub-frontend service. Click on step 3 "Frontend configuration". You should land on the following page.
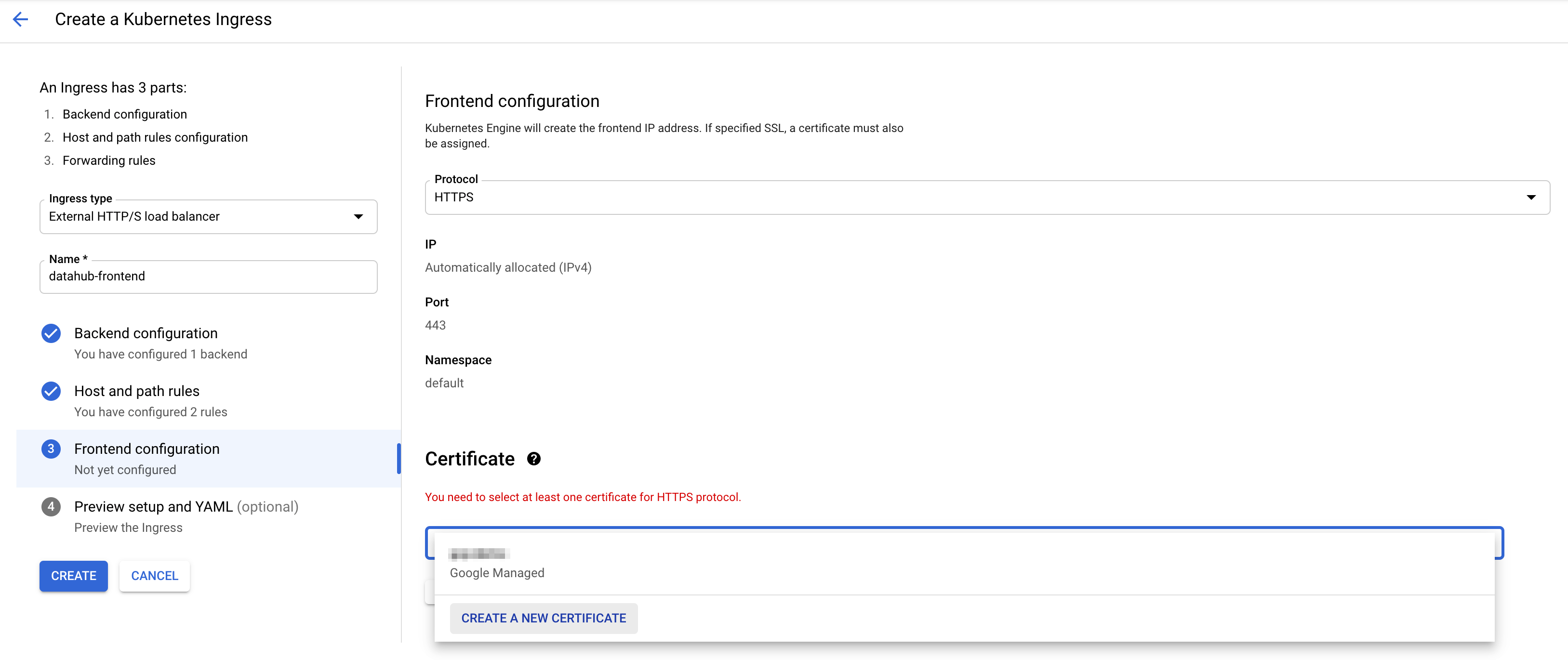
Choose HTTPS in the dropdown menu for protocol. To enable SSL, you need to add a certificate. If you do not have one, you can click "CREATE A NEW CERTIFICATE" and input the host name of choice. GCP will create a certificate for you.
Now press "CREATE" button on the left to create ingress! After around 5 minutes, you should see the following.
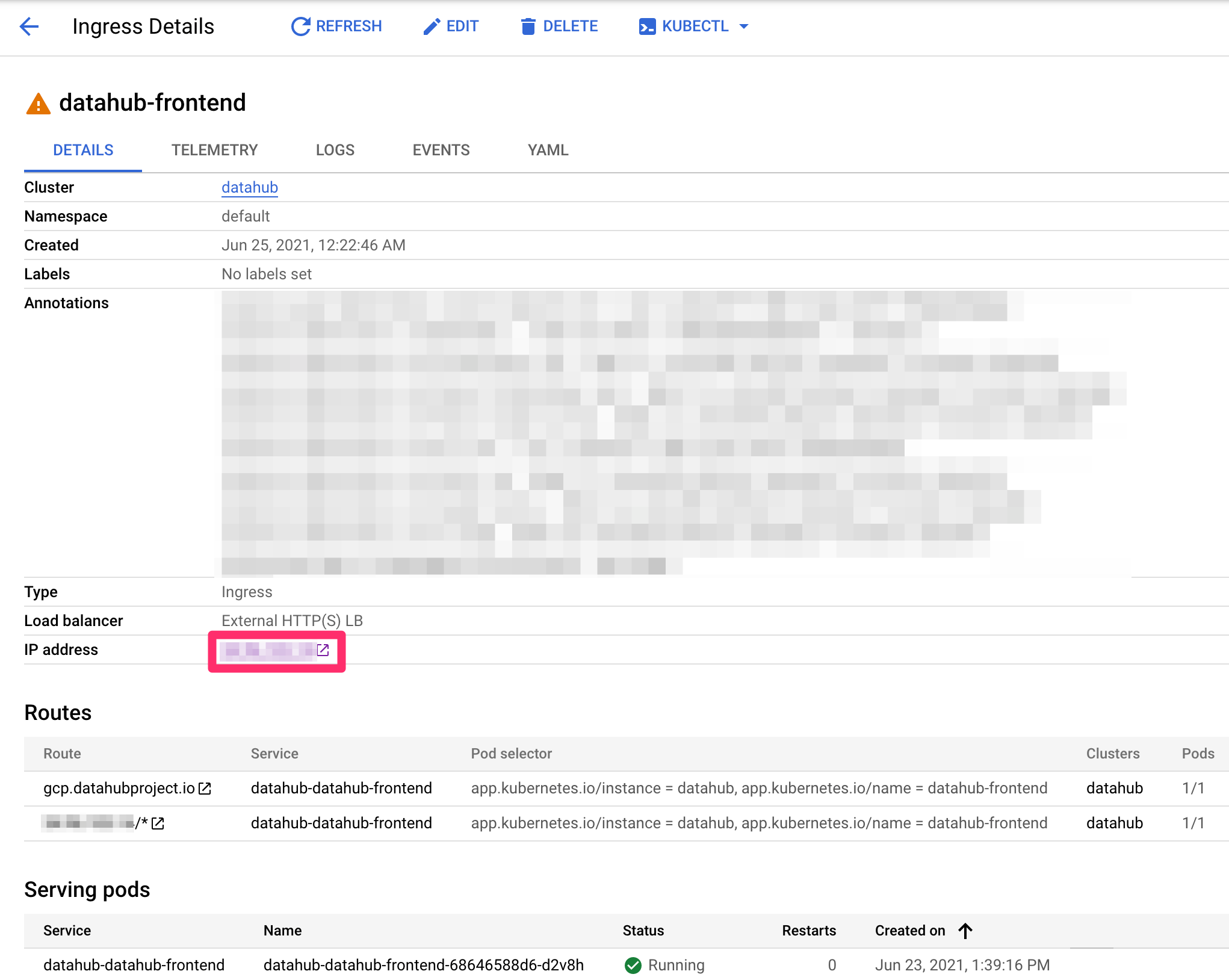
In your domain provider, add an A record for the host name set above using the IP address on the ingress page (noted with the red box). Once DNS updates, you should be able to access DataHub through the host name!!
Note, ignore the warning icon next to ingress. It takes about ten minutes for ingress to check that the backend service is ready and show a check mark as follows. However, ingress is fully functional once you see the above page.

